You’ve probably noticed that a lot of roofs have blue solar panels.
However, there are black panels as well.
So, why are solar panels blue? The color differences are due to the type of panel and how it reacts to light.
To better understand solar panel colors, one must consider the two main types of panels. These are monocrystalline and polycrystalline panels. But, there is also a third type known as thin-film solar panels, although not common.
In this article, we’ll explain the different solar panels and their colors.
Understanding Solar Panels
Photovoltaic cells form the basis of solar panels. The most popular material for solar panels is silicon.
Silicon is a hard and brittle crystalline substance that is abundant on Earth. Although silicon isn’t metal, it has conductive abilities.
It is this feature that helps a solar panel convert sunlight into energy.
Also, most manufacturers use silicon because it’s affordable.
So, How Does It All Work?
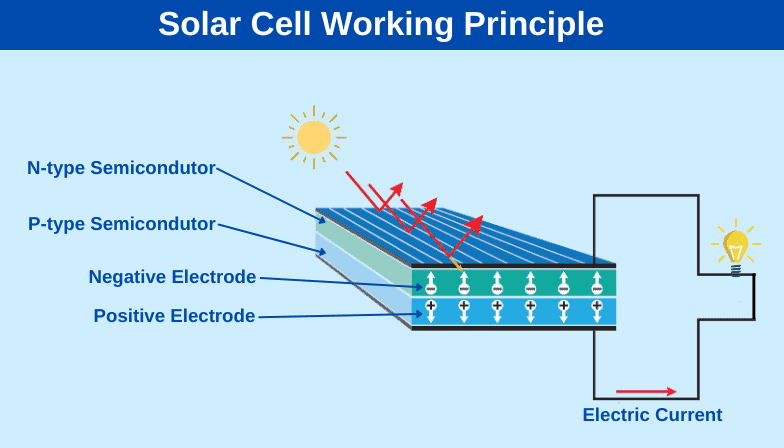
A PV cell is like a sandwich, with silicon on either side. These cells work by creating an electric field.
To do this, manufacturers create a field by doping each side of the silicon with different materials, creating a negative (n-type) and a positive (p-type) side.
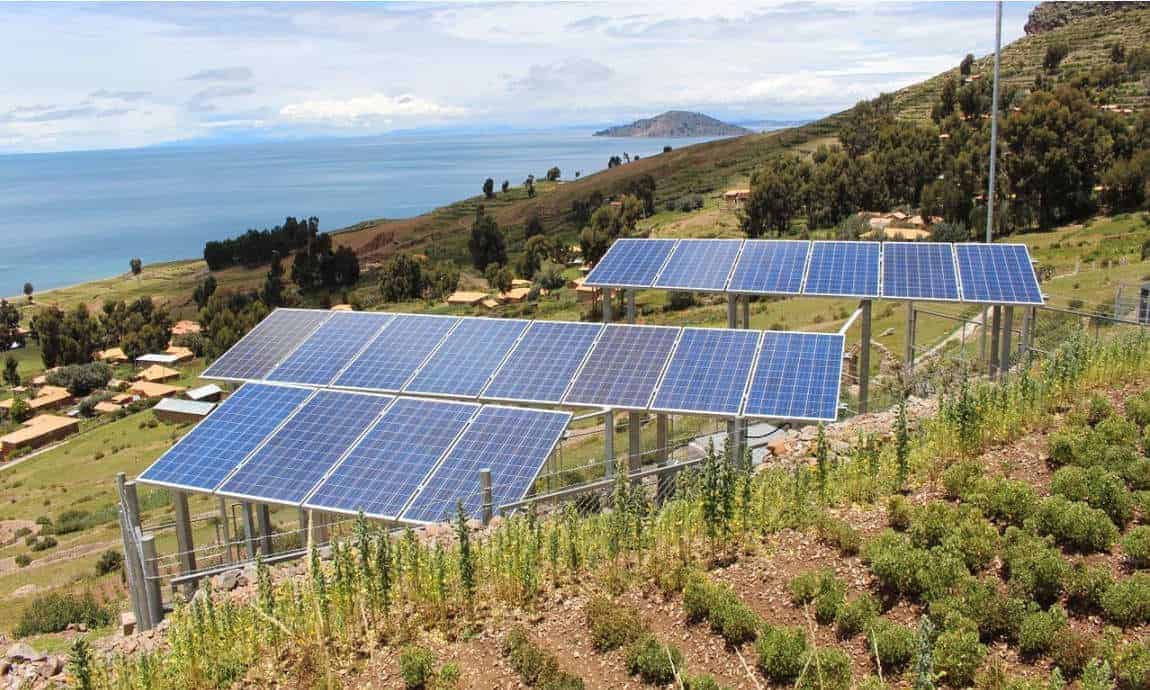
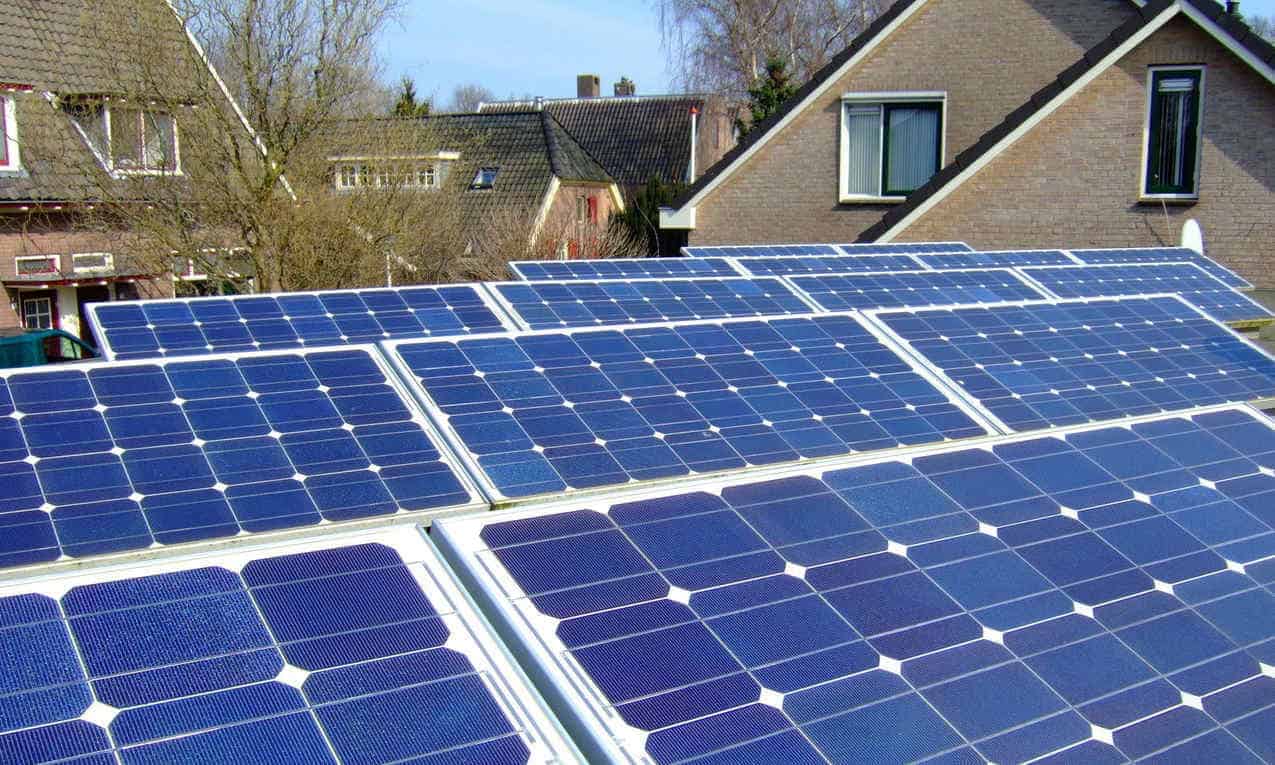
Blue Solar Panels (Polycrystalline)
Polycrystalline panels, the most common ones, are blue. The blue is a result of the multiple silicons used to make them.
The panels have an anti-reflective coating that reduces reflection to maximize light absorption. This quality improves their ability to absorb light and function better.
To make polycrystalline panels, manufacturers put together many silicon crystals and melt them. Once melted in a crucible, the silicon is poured into a mold to form the polycrystalline structure.
This molten silicon is then allowed to cool. A seed crystal is added to the mixture for the formation of the structure. These are then joined again to form the panel.
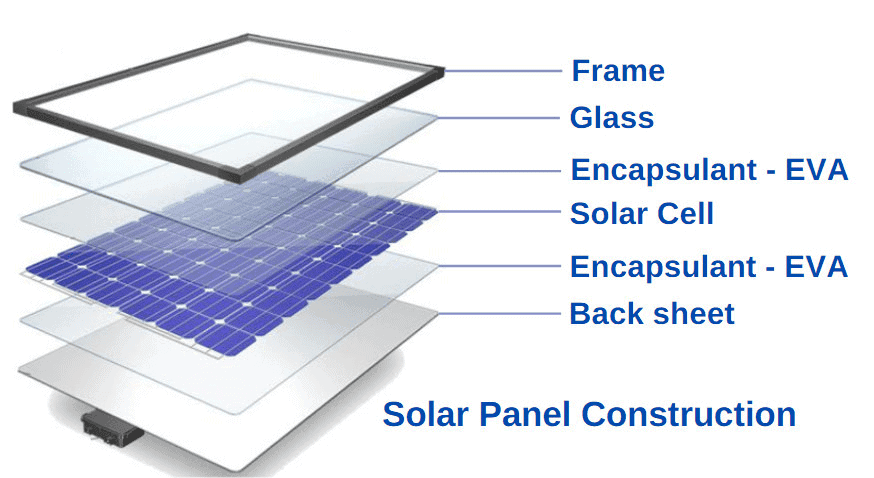
Although the panels are blue, polycrystalline frames are usually silver. The back sheets can either be white or silver.
The benefits of using polycrystalline panels
- They absorb light well – Because of the silicon material used to make them, polycrystalline panels have reasonably good efficiency.
- They cost less – Polycrystalline panels have a more straightforward manufacturing process. This simpler method results in less wastage compared to monocrystalline ones. Their cost is slightly lower, around $3 per watt. The result is a cheaper panel, which is affordable for those with small and medium-sized roofs.
- Their blue color – Some people find these panels more aesthetically pleasing. Therefore, they prefer to use them on their roofs.
- Good for the environment – Although this feature doesn’t apply to all polycrystalline panels, some manufacturers protect the environment. These makers of polycrystalline panels use advanced technologies that do away with soldering.
The downside of polycrystalline panels
- Reduced efficiency – Solar cells used in polycrystalline panels are less efficient than those of monocrystalline panels.
- Easily broken – Polycrystalline panels can be broken by heavy objects when it’s windy, making them fragile.
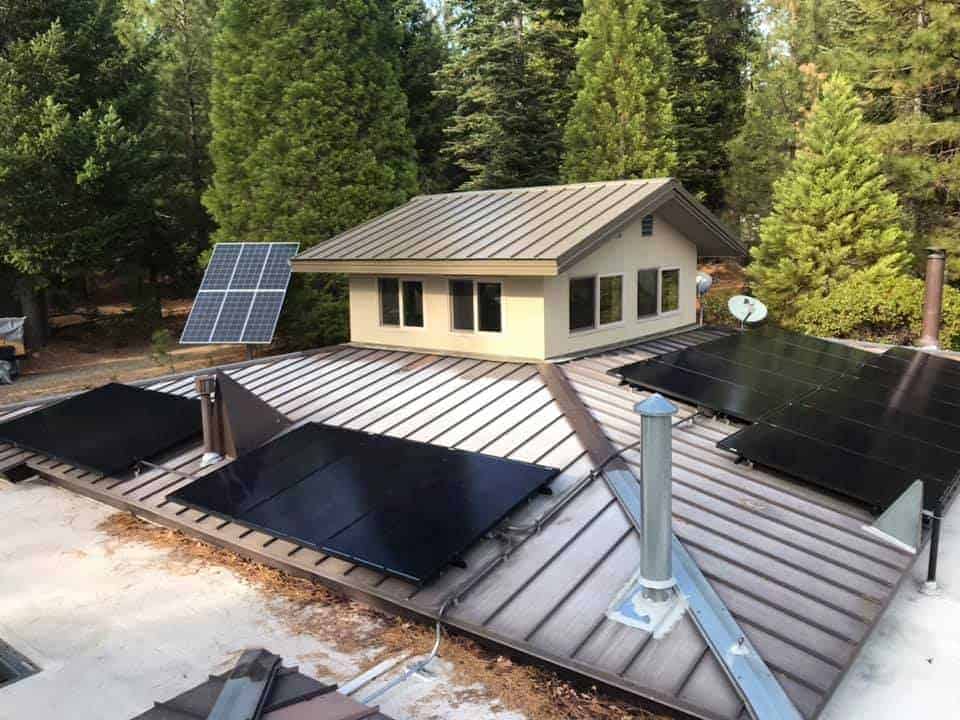
Black Solar Panels (Monocrystalline)
With monocrystalline panels, manufacturers use one silicon crystal to make each solar cell. They use about 40 solar cells made of pure silicon.
The manufacturing method makes use of the Czochralski process. In this technique, single crystals are taken from semiconductors like silicon.
To do this, you melt silicon, from which you lift a silicon seed. Moving it out of the dish causes the silicon to form a bigger crystal.
These larger crystals are cut into squares or wafers to make solar cells for the monocrystalline panels.
The downside of this technique is that there’s waste of silicon.
Monocrystalline panels produce higher power than the rest because they are also sold in more wattage. Currently, you can find monocrystalline panels with a capacity of over 400W.
At $6 per watt, monocrystalline panels are the most expensive.
Their black color is a result of their interaction with light. Usually, the panels’ metal frame is silver or black. But, the back sheets color can match the cell or come in white or silver.
The benefits of using monocrystalline panels
- More efficient – Monocrystalline panels have a 15-20% efficiency. Monocrystalline solar cells can convert a large amount of solar energy into electricity. This feature comes in handy if you want to produce high wattage from a single area such as your roof. They are also the best in areas with low sunlight.
- Less space – These panels don’t use up a lot of space compared to polycrystalline panels. This aspect makes them ideal for those who live in cities.
- Durability – They last longer, with most of their warranties being 25 years. The technology used to make monocrystalline panels has been around for decades, making them more trustworthy. Panels installed in the 70s are still said to be in use. The only thing to note is that their efficiency has dropped over the years.
- Cost less to install – Solar panels are not only expensive but can be costly to install. The good news is that monocrystalline panels have lower mounting costs. Sometimes it takes more rails to mount other types of panels. Other times, you have to remove all your panels when you want to move to a different type.
- Environment-friendly – Unlike other panels, monocrystalline panels are not harmful to the environment. Some solar products with a thin film are known to produce a harmful heavy metal – cadmium telluride (CdTe). This metal is only dangerous when you want to dispose of your panels after reaching their end of life.
The downside of monocrystalline panels
- More Expensive – Because their manufacturing requires more work, monocrystalline panels cost more.
- High-temperature hitch – They tend to perform poorly with increased temperatures. However, the energy loss is minimal.
- More wastage – A lot of material goes to waste during their manufacturing.
Thin-Film Solar Panels
These panels are a new entry into the market and can be blue or black, depending on their material.
Unlike monocrystalline and polycrystalline panels, thin-film ones do not always have silicon.
Cadmium telluride is the most common material for thin-film solar panels. Others are amorphous silicon and Copper Indium Gallium Selenide. The silicon in the amorphous type is not crystalline.
How are they made? You place the core material between a conductor and cover it with glass for protection.
While a thin-film panel is thinner than the crystalline types, you still have to consider the frame size. A thin-film panel plus its frame can be the same size as poly and monocrystalline panels.
The benefits of using thin-film solar panels
- Cheapest around – Due to their thin profile, thin-film panels are cheaper to install than crystalline panels. At between $2 and $4, thin-film solar panels are the cheapest in the market.
- Not limited by materials – Makers use various materials for thin-film solar panels, such as Cadmium telluride and amorphous silicon.
- Weight advantage – While crystalline panels are up to 200mm thick, thin-film ones are 1mm. This quality means you can mount them even on a weak roof without fear of damage.
- High tolerance to temperature – Unlike crystalline panels, which start losing their efficiency at 25 degrees Celsius, thin-film ones are not affected much by heat.
- Are flexible – This feature means you can install thin-film panels even on sophisticated roofs.
The downside of thin-film solar panels
- Less efficient – Compared to other panels, thin-film ones have a lower efficiency of up to 13%.
- Space requirements – Although they are flexible, thin-film solar panels need more space to achieve the same efficiency as crystalline panels. If you have a small roof, they might not be ideal.
- Shorter lifespan – Because they age faster, you will get a lower warranty for thin-film solar panels.
Which Way? Blue Vs. Black Solar Panels
By going solar, you save money you’d have spent on electricity bills.
However, there are various reasons to choose one type of solar panel and not the other.
Aesthetics considerations
Because polycrystalline and monocrystalline panels have different colors, your choice may be based on this.
Some people find polycrystalline panels more appealing than monocrystalline ones due to their blue color. The preference is despite the cost differences.
Available space
You can go for monocrystalline panels if you have limited space. Besides, they still produce more electricity. However, if you have a big roof or want to mount it on the ground, polycrystalline panels might be ideal for you.
Funding system
Different financing plans can influence your panel choice. A power purchase agreement plan uses the per-kilowatt-hour payment mode.
On the other hand, monocrystalline panels are the best when buying your system. Why? Your returns will be higher.
Summary
Why are solar panels blue? The simple answer to that is that the hue results from how light interacts with different types of panels.
Polycrystalline panels are usually blue. The bluish hue results from the light reflecting on the polycrystalline cell, which is different from the way it does on monocrystalline panels.
On the other hand, monocrystalline panels have black cells hence their appearance. But, their back sheets are of different colors, from black to silver.
Further, thin-film solar panels can come in different colors. They can be black or blue.
Your choice of solar panels depends on various factors from color and space available, to cost.